Transmission Media:
What is Transmission Media?
Transmission Media is the actual physical media that carries signals. These signals can either be electrical or electromagnetic. Electrical signals are simple currents carrying some voltage values while electromagnetic signals are waves. A transmission media is the one thing that can carry either of these two.
Types of transmission Media:
- Guided / Wired Media.
- Unguided / Wireless Media.
Guided Media:
This media includes wires. Some of the wires are copper wires and hence carry electrical signals whereas some are glass core wires capable to carry optical rays. The copper wires are: TPC and Co-axial cable. The only glass core wire is OFC.
Guided Media is of following three types:
- TPC (Twisted Pair Cable).
- Co-Axial Cable.
- OFC (Optical Fiber Cable).
TPC (Twisted Pair Cable):
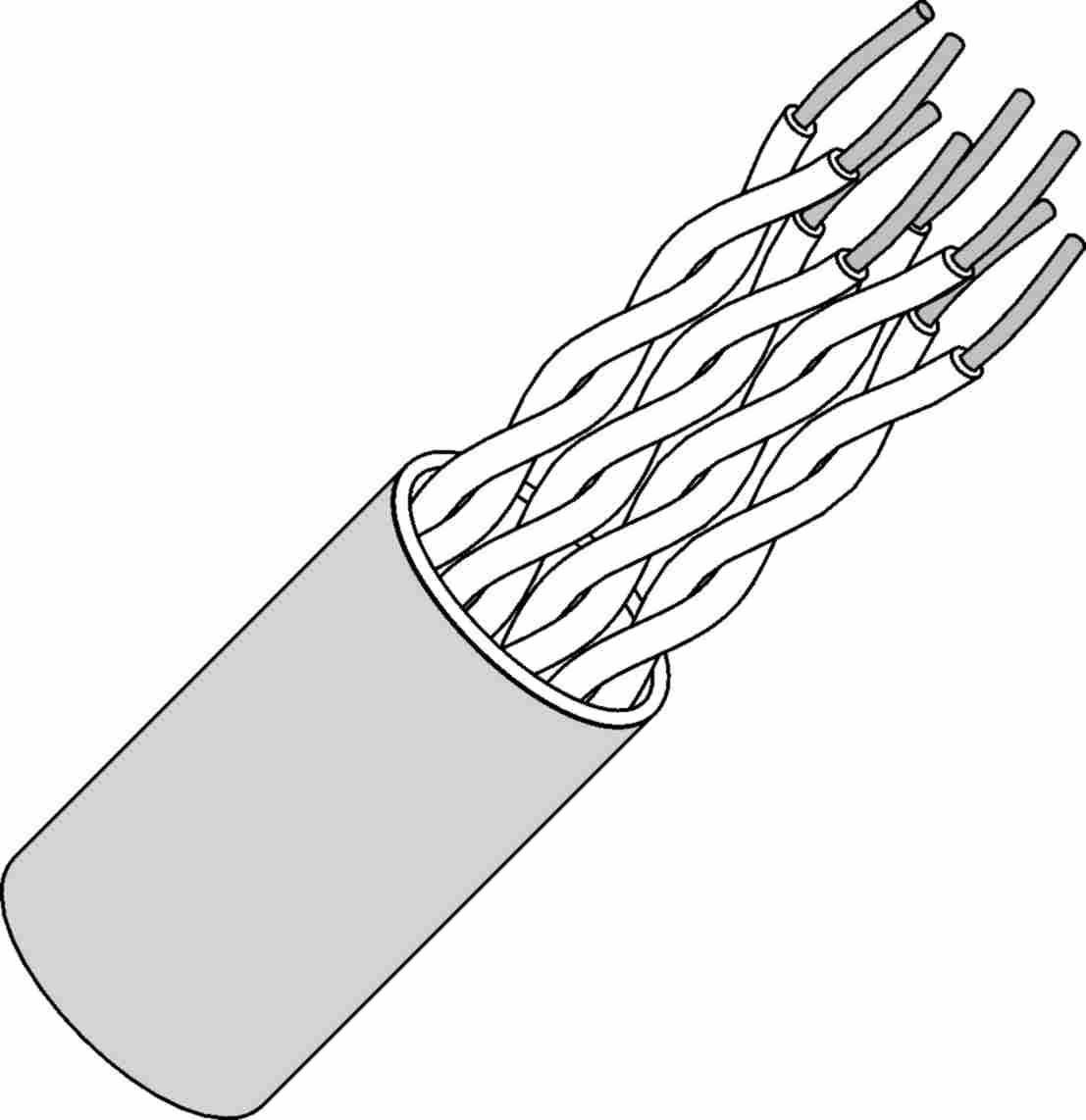
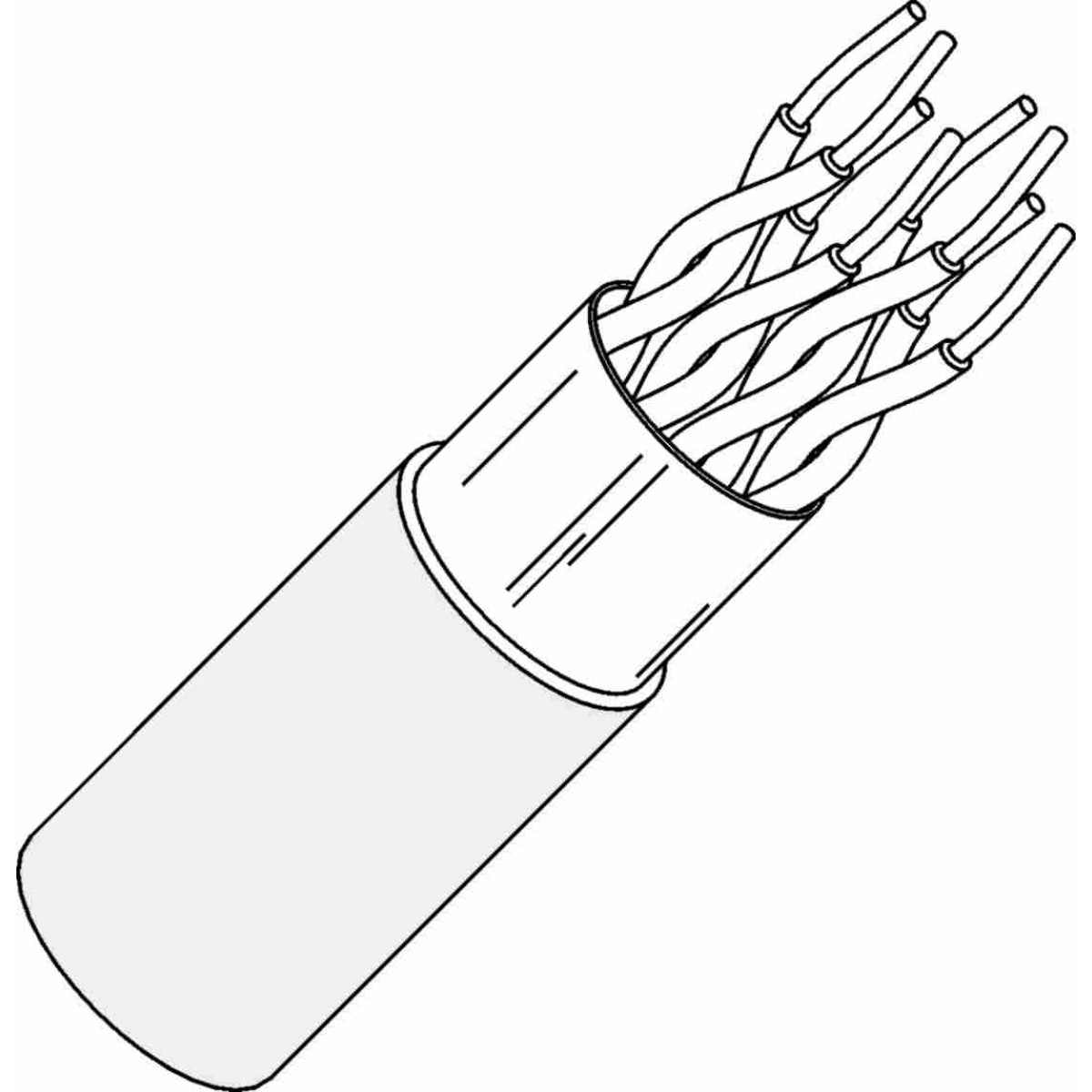
TPC is the mostly used cable in a LAN. It contains 8 wires twisted in pairs of two. Thus four pairs are there out of which, only 4 wires (one of each pair) carry signals whereas remaining four are just for ground reference.
The pairs are as below:
TPCs are of two types:
- 1. UTP: UTP is the most common wire used as TPC. It has all 8 wires covered in a rubber jacket.
- 2. STP: STP is the innovation used by IBM in TPC. In these cables, there is a shield that contains the wires. The shield is further covered in a jacket.
NOTE: UTP/STP both use RJ-45 as connectors. The maximum distance that is covered by these cables is 100 meters.
Co-Axial Cable:
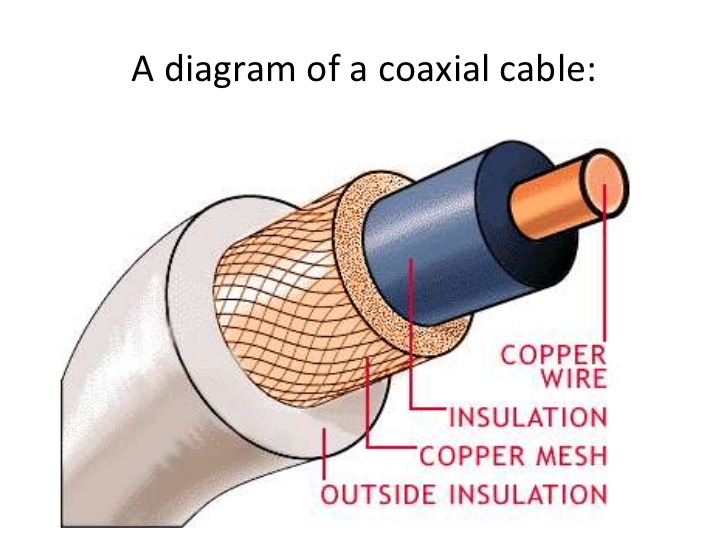
Co-axial cable is a different kind of cable that uses only one central copper core. All signals travel through that core. Here the outer cover is a jacket inside of which, there is a metallic mesh. Inside of mesh, there is a PVC shield that covers the copper core.
These cables are not much used in LANs. Instead, these cables are used in TV networks. The high bandwidth makes it compatible to be used for heavy video data in TV networks.
These cables are of two types:
- Thicknet (covers 500 meter distance)
- Thinnet (covers 200 meter distance) but 180m mostly.
NOTE: CO-axial cables use BNC connectors. BNC is the group of characters that define the names of its inventors. Buyonet, Neill and Concelman were the inventors of BNC.
Optical Fiber Cable:
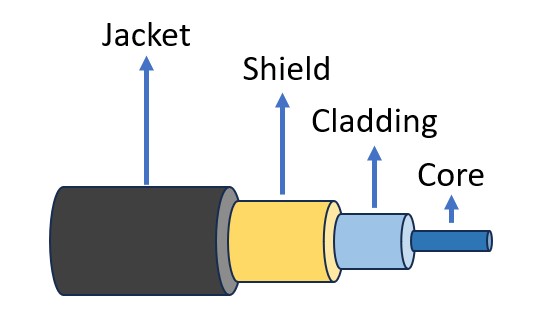
OFC stands for Optical Fiber Cable. It is a cable with a glass core in it that can pass optical rays through it. The structure of this cable consists of a jacket in which there is a PVC shield. Inside of the shield, there is a layer of cladding. The glass core is packed in this cladding.
OFC is mostly used in long distance communication. For example- Intercity LAN connections, Intercontinental communication using deep sea cabling.
OFCs are of following two types:
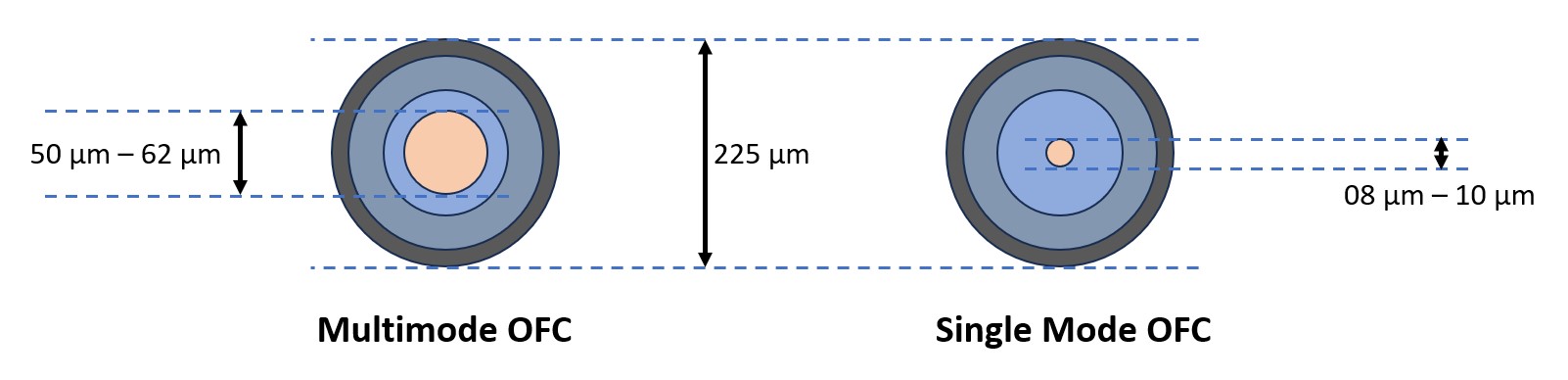
- Single mode OFC
- Multimode OFC
Single mode OFC is the one that contains just one glass core in the cladding whereas multimode OFC is the one that may have many glass cores inside of one single OFC.
NOTE: OFCs use two very specific connectors namely SC (Secure Connection) and ST (Secure Tip) connectors. These are tailor made.
Unguided Media:
The media that has no any guided path to travel is known as unguided media. Since EM waves travel in Arial direction, these are all included in unguided media.
The waves in unguided media are as follows:
- Radio Waves
- Micro waves
- Infrared Rays
Radio Waves:
Radio waves are the EM waves of the frequency range: 3 KHz – 100MHz. This low frequency enables these waves to travel Omni-directional, up to long distances with a very high penetration power. Due to these properties, Radio waves are used extensively in TV and Radio communication.
A dish antenna is needed to receive the signals sent by the sender.
Micro Waves:
These are the waves of frequency range: 300MHz – 300GHz. This medieval frequency range enables the waves to travel medium distances with a focused behavior and a medium penetration power. The distance cover is also a little short than Radio waves. Microwaves are used in Cellular telephony and Bluetooth kind of networks.
Horn antennas are used to receive the Microwave signals.
Infrared Rays:
Infrared is the very high frequency wave. The range starts from 300GHz to 400THz. Distance cover is very short (in feet). Propagation is in straight line and penetration power is NIL. Infrared is used in short-distance device to device communications like Remote to TV etc.
LED (Light Emitting Diode) and LDR (Light Detecting Resistance) are used as antenna in Infrared communication.